By Jeanne F. Neath
Perhaps after reading the first half of this blog, the subsistence economy has begun to feel familiar to you. Or not. Whatever you may be feeling, the fact remains that the male-dominated economy is doing us – Earth and humans – in and there is an already existing woman-centered economy that can take its place. Part 2 of this blog is again primarily written for people of the global North (“North” and “South” here refer more to the “developed” vs. “developing” world than to strict geographies. Even within a country, some groups may belong to the North and others to the South.) [1]. We have a choice to make!
The War Against Subsistence
The capitalist, colonizing patriarchy is doing everything it can to control that choice. This global system does not want anyone, global South or North, to have “an independent subsistence”. As Mies and Bennholdt-Thomsen explain:
“Ivan Illich stated as long ago as 1982 that the war against subsistence is the real war of capital, not the struggle against the unions and their wage demands. Only after people’s capacity to subsist is destroyed, are they totally and unconditionally in the power of capital.” (p. 19, Subsistence Perspective, Maria Mies and Veronika Bennholdt-Thomsen)

In the global South vast numbers of people from the countryside have been forced from their lands and subsistence-based ways of life as result of centuries of colonization, international development policies, land and water grabs, loss of land due to climate and ecological disasters, and corporate/state pressures on peasant farmers.
In the global North over a century of economic pressures on small farmers, propaganda campaigns portraying rural life as backwards and the industrialization of agriculture have pushed many farm families off their lands.[2] Today the “service” economy is busily eating away at the subsistence economy, as people pay for all kinds of things they used to get from their communities, do for themselves or not do at all, including “treating themselves” to toenail and fingernail manicures, socializing on social media, getting tattoos, and eating at fast food restaurants, to name a few.
The capitalist economy is colonizing and commercializing both the Earth and the subsistence economy in its endless quest for profit and wealth for the few. Resistance is strong in the global South, but people in the global North are far more under the control of capital, due to our loss of “an independent subsistence.”
The capitalist economy is colonizing and commercializing both the Earth and the subsistence economy in its endless quest for profit and wealth for the few.[3] Resistance is strong in the global South, but people in the global North are far more under the control of capital, due to our loss of “an independent subsistence.”
Putting Women at the Center
Still, the woman-centered economy beckons. Every day women (and men) in the industrialized world get to choose the economy they want over and over again. Eat out (capitalism) or cook dinner (subsistence). Plant kale or buy it at Wal-Mart. Walk the dog or hire a dog walker. Through making one choice at a time women (and men) can gradually diminish our dependency on and support for the male-dominated economy.
 Putting women at the center of an economy prevents men from taking more than their share of power and ensures a balance between women and men. Woman-centered does not imply woman-dominated. Women in subsistence economies (and elsewhere) generally create caring and sharing relationships that are non-hierarchical.
Putting women at the center of an economy prevents men from taking more than their share of power and ensures a balance between women and men. Woman-centered does not imply woman-dominated. Women in subsistence economies (and elsewhere) generally create caring and sharing relationships that are non-hierarchical.
Our individual choices give us power in our own lives, but subsistence economies are created by communities of people giving to and receiving from each other and the Earth. The giving of gifts begins with the gifts of the Earth and the gifts of human mothers. As Robin Wall Kimmerer has explained, a natural human response to “a world made of gifts”, the abundance of nature, is to also give, give to the Earth and to each other.[4] Among humans, gift giving comes very naturally since human infants are dependent on the care – gifts – of our biological and social mothers. According to Genevieve Vaughan, this one-way mother/child gifting relationship forms the basis of a maternal gift economy where all relationships are based in gifts, not exchanges.[5]
Subsistence economies are based in the giving of gifts, though some, perhaps the more stratified and patriarchal ones, may include barter, trade, cash and markets while still making the well-being of everyone in the community the central concern.[6] In many subsistence-based societies women participate in local markets in order to share surpluses from subsistence production and gain power and prestige within their communities.[7] Increasingly, feminists interested in a return to subsistence and maternal gift economies are acknowledging the connections between the two.[8] Perhaps a better name for the subsistence economy would be the “subsistence/gift economy.”

The capitalist economy isolates people and destroys community. Both gift giving and subsistence-based relations create deep bonds and community. As female-centered economies grow, we can expect communities to grow and strengthen too. With a central place in the economy, women’s place in community should follow suit.
We can choose to create community at the same time we choose the subsistence/gift economy over capitalism. Yes, cook dinner instead of eating out AND invite family, friends or neighbors. Plant kale, eat it yourself AND give some away. Do this within the community you belong to or intentionally begin creating the community you want.
A Plan for Transformation
Despite the climate and larger ecological emergencies unfolding, this dominant society is not even attempting to create a plan that would make the radical (meaning root) transformations necessary to halt these disasters. Such a plan would have to recognize the need to bring capitalism, growth, male dominance and all domination to an end. This the power holders in the global society cannot and will not even consider.
Despite the climate and larger ecological emergencies unfolding, this dominant society is not even attempting to create a plan that would make the radical (root) transformations necessary to halt these disasters. Such a plan would have to recognize the need to bring capitalism, growth, male dominance and all domination to an end. This the power holders in the global society cannot and will not even consider.
As Veronika Bennholdt-Thomsen has explained, these times call for new strategies to create social change:
“In view of the social power structures of our era, the old quandary of whether “we” should abolish the plundering capitalist system or whether “we” – since there is no time for systemic issues – should concentrate on reforms, has become obsolete. What matters now is that we – all sovereign individuals capable of acting responsibly – withdraw from the forced maximization economy by refusing to participate.”[9]
A very promising option available to those in the global North who want radical transformation is constructive resistance, the use of actions that work to both upend capitalist, colonizing patriarchy and, at the same time, create alternatives. Reclaiming and expanding woman-centered economies is constructive resistance. Every move into the female-centered economy is a move out of the male-dominated economy. Because capitalism is dependent on growth (to avoid recession, depression, collapse), it depends on women’s (and other consumers’) participation.[10] Think back to George W. Bush’s response to 9/11. Here in the U.S. we were told to go shopping!
Every move into the female-centered economy is a move out of the male-dominated economy. Because capitalism is dependent on growth (to avoid recession, depression, collapse), it depends on women’s (and other consumers’) participation.
The male-dominated economy has an Achilles’ heel. The growth of the woman-centered economy is the dart that can slow it down and, over time, bring it to an end. Talk of ending the economy that so many people now depend on sniffs of disaster, yet so does the continuation of that economy. An alternative way to meet everyone’s needs must be created. That alternative is the subsistence/gift economy! The shift to this woman-centered economy opens the door to the creation of fully woman-centered communities and societies that do away with domination.
 Why not switch to the female-centered economy and scrap the male-dominated one? Clearly, the male-dominated economy that is bringing us climate catastrophe, forced migrations and the Sixth Extinction is far scarier than the subsistence/gift economy that exists only to bring us life. In the global South, people have been fighting to continue their own ways of life, which includes their subsistence economies, since the beginnings of colonization. Choosing to embrace and expand woman-centered economies offers those in the global North another way to step up by moving into an Earth-centered way of life and curtailing support for the economy of destruction.
Why not switch to the female-centered economy and scrap the male-dominated one? Clearly, the male-dominated economy that is bringing us climate catastrophe, forced migrations and the Sixth Extinction is far scarier than the subsistence/gift economy that exists only to bring us life. In the global South, people have been fighting to continue their own ways of life, which includes their subsistence economies, since the beginnings of colonization. Choosing to embrace and expand woman-centered economies offers those in the global North another way to step up by moving into an Earth-centered way of life and curtailing support for the economy of destruction.
If you are still troubled by thoughts of what you might have to give up as the male-dominated economy winds down, consider this. Yes, subsistence economies provide the essentials of life, not the “extras.” But, there can be more than one economy, a mix of economies, within any society. Why not have two female-centered economies? Caring for the well-being of all Earth and human communities must be the priority, but as the earth recovers, woman-centered economies providing “wants” may evolve and co-exist with subsistence economies.
Gardening and Eating: A First Step
Industrial agriculture is terrible for the Earth.[11] We have to eat! Industrial agriculture – a central part of the male-dominated economy – must be replaced and we can look to the woman-centered economy for the replacement.
 Mountain Mother is calling me and it’s spring so the earthworms and the garden are calling extra loud. If you listen, you will probably hear them too. Not everyone is physically able to garden, but everyone can probably find a way to make sure their food scraps feed the earthworms and restore the soil.
Mountain Mother is calling me and it’s spring so the earthworms and the garden are calling extra loud. If you listen, you will probably hear them too. Not everyone is physically able to garden, but everyone can probably find a way to make sure their food scraps feed the earthworms and restore the soil.
With most women (and men) in the U.S. spending so little time gardening (average is under 1 ½ hours a week for women) there is a great opportunity to expand home food production. This expansion could happen really quickly, as it did during both World Wars when the U.S. government encouraged people to plant victory gardens. In 1943, 20 million victory gardens produced 10 billion pounds of food.
Hello earthworms! Creating home and community gardens and small farms can restore the Earth and restore us. There is plenty of work to be done besides the actual gardening, including garden planning, learning about insects, seed saving, cooking and preserving foods and much more. As we become deeply connected to the plant world, our relationships with the life-giving soils and ever-changing winds and waters will grow too. These kinds of deep and real connections can transform our lives, including even our desires and what we think we need. Stepping away from the cell phones and all the rest of the constant bombardment of modern society and slowing down to nature’s pace can open up such a different and awesome world that everything changes, inside and out.
This reminds me of one last insight from Veronika Bennholdt-Thomsen:
“Decommercialization is first and foremost an attitude of mind. Orienting ourselves not to money, but to what we actually need puts all decisions in a new light. Modern insatiability can be replaced by the satisfaction of having a need fulfilled.”[12]
Notes
1. “inequality within countries has also been growing and some commentators now talk of a ‘Global North’ and a ‘Global South’ referring respectively to richer or poorer communities which are found both within and between countries. For example, whilst India is still home to the largest concentration of poor people in a single nation it also has a very sizable middle class and a very rich elite.” More info here.
*****
2. Maria Mies and Veronika Bennholdt-Thomsen, The Subsistence Perspective, p. 17-19.
*****
3. “Money or Life? What Really Makes Us Rich” by Veronika Bennholdt-Thomsen in Climate Chaos: Ecofeminism and the Land Question edited by Ana Isla, 2019.
*****
4. “Mishkos Kenomagwen, The Lessons of Grass” by Robin Wall Kimmerer in Traditional Ecological Knowledge: Learning from Indigenous Practices for Environmental Sustainability edited by Melissa K. Nelson and Dan Shilling, 2018
*****
5. Genevieve Vaughan, For-Giving: A Feminist Criticism of Exchange, 1997.
*****
6. For example, Mies and Bennholdt-Thomsen described how a peasant and craft economy functioned as late as the 1960s in the German village of Borgentreich. Peasants traded their farm products for the goods and services of local craftspeople: blacksmiths, dressmakers, bakers, carpenters and so on. Cash payments were only required when the craftsperson had to buy materials (e.g. fabric) and needed to replace the cash they had spent. But, not every person could pay. Then as Mies and Bennholdt-Thomsen report:
“After waiting in vain, the craftsman would sometimes go to the farmer and pick up a couple of sacks of rye or seed, or maybe a few piglets. But, as one master joiner put it, ‘We also simply forgot about a lot of it.’ The baker said that most people paid their bills at the end of the year, but ‘those who hadn’t a penny to their name got their bread for nothing; in the end you couldn’t just let people starve.’” From Maria Mies and Veronika Bennholdt-Thomsen, The Subsistence Perspective, p. 88-89.
*****
7. Maria Mies and Veronika Bennholdt-Thomsen, The Subsistence Perspective, p. 109-110.
*****
8. For example, Veronika Bennholdt-Thomsen includes a discussion of the maternal gift economy in her 2019 article “Money or Life? What Really Makes Us Rich” published in the Climate Chaos anthology edited by Ana Isla.
*****
9. “Money or Life? What Really Makes Us Rich” by Veronika Bennholdt-Thomsen in Climate Chaos: Ecofeminism and the Land Question edited by Ana Isla, 2019. p. 55.
*****
10. David Holmgren, one of the founders of permaculture, suggests in his article “Crash on Demand” that permaculture activists could initiate a financial crash by reducing consumption and that this could bring about desperately needed societal and ecological changes. Holmgren’s ideas are very interesting, yet have received sharp criticism from some because of the effects a financial crash would have on humans. I am suggesting a gentler approach than Holmgren in which the growth of the subsistence economy would supply people with what we need to live as the capitalist economy (and the damages created by it) diminish through reduced participation. Withdrawing from the capitalist economy and is a matter of ethics! In either Holmgren’s scenario or the one I am suggesting, the actions of a relatively small portion of the populace could have a large effect because of capitalism’s fragility.
*****
11. Industrial agriculture is not only a major contributor to climate change, but also fuels habitat loss, the biodiversity crisis, freshwater drawdown, pollution and more. For an introduction to these issues, check this out
*****
12. “Money or Life? What Really Makes Us Rich” by Veronika Bennholdt-Thomsen in Climate Chaos: Ecofeminism and the Land Question edited by Ana Isla, 2019. p. 60.
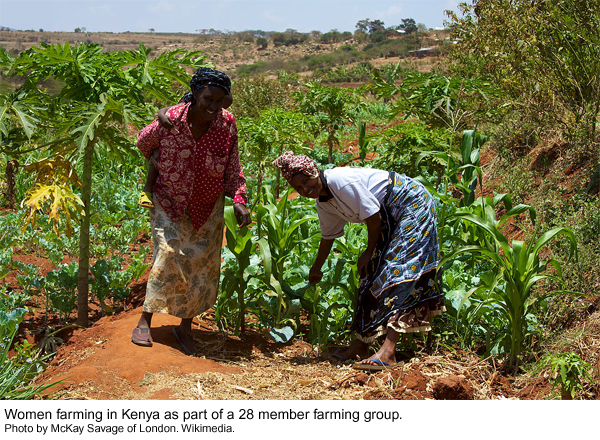


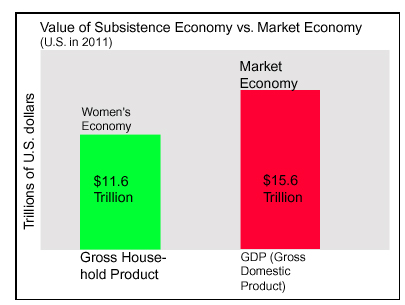 It is important to understand the importance and the size of the subsistence economy. Genevieve Vaughan recently discussed research from D. Ironmonger and F. Soupourmas showing that unpaid household work, called “gross household product”, would have cost $11.6 trillion in 2011, if wages had been paid.
It is important to understand the importance and the size of the subsistence economy. Genevieve Vaughan recently discussed research from D. Ironmonger and F. Soupourmas showing that unpaid household work, called “gross household product”, would have cost $11.6 trillion in 2011, if wages had been paid. Maintaining life involves much more than socializing the next generation and women do much of this maintenance work too, even in the global North. You don’t have to have children to play a central role in running a household. For example, do you cook meals? Clean your house? Care for other members of your household when they are sick? Walk the dog? Do yard work? Sew buttons back on your clothes when they fall off? Keeping a household going can involve seemingly endless work and women do much of it! This is true even in households that have many modern “conveniences.”
Maintaining life involves much more than socializing the next generation and women do much of this maintenance work too, even in the global North. You don’t have to have children to play a central role in running a household. For example, do you cook meals? Clean your house? Care for other members of your household when they are sick? Walk the dog? Do yard work? Sew buttons back on your clothes when they fall off? Keeping a household going can involve seemingly endless work and women do much of it! This is true even in households that have many modern “conveniences.” We can’t include anyone’s production work from the capitalist economy (in jobs, as business owners) in these considerations as that work isn’t subsistence work and cuts into time available for subsistence work.
We can’t include anyone’s production work from the capitalist economy (in jobs, as business owners) in these considerations as that work isn’t subsistence work and cuts into time available for subsistence work.



